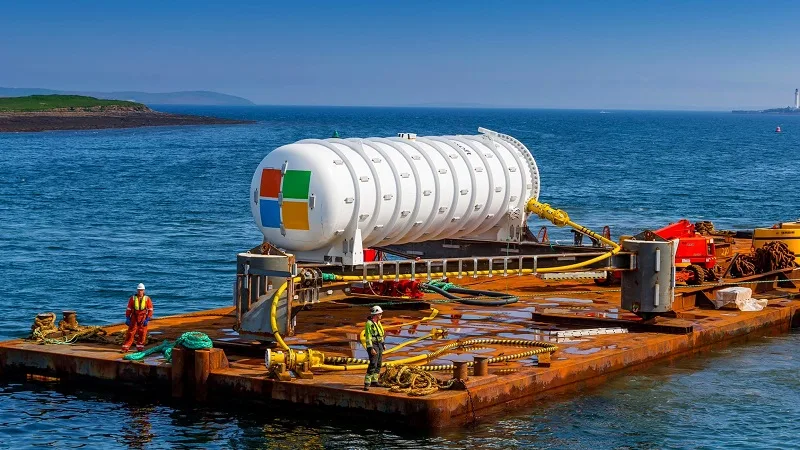
Data Centers Underwater: The Future of Sustainable Technology
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, data centers are the backbone that supports the increasing demand for data storage and processing. With the advent of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the need for efficient and sustainable data centers has never been more critical. One innovative approach gaining traction is the concept of underwater data centers. This article explores what data centers are, how underwater data centers work, why companies are considering this approach, the advantages and disadvantages, and the potential future of this technology.
What is a Data Center?
A data center is a facility that houses computing and storage resources, enabling the delivery of shared applications and data. These facilities typically include servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and other infrastructure necessary for managing and processing large volumes of data. Data centers are essential for a variety of services, including cloud computing, enterprise applications, and internet services.
Modern data centers are designed to ensure high availability, security, and efficient operation. They employ advanced cooling systems, redundant power supplies, and sophisticated security measures to protect sensitive information. As the demand for data storage and processing continues to grow, the need for scalable and sustainable data center solutions becomes increasingly important.
How Underwater Data Centers Work
Underwater data centers operate by submerging data center modules in the ocean. These modules are encased in waterproof containers and placed on the seabed. The ocean’s natural cooling properties help dissipate the heat generated by the servers, reducing the need for traditional cooling systems and significantly lowering energy consumption.
The concept of underwater data centers leverages the cold temperature of deep ocean water to achieve more efficient cooling. This method not only reduces the environmental impact but also cuts operational costs. Additionally, underwater data centers can be powered by renewable energy sources such as tidal or wave energy, further enhancing their sustainability.
Why Consider Launching Data Centers Underwater?
The idea of launching underwater data centers stems from the need to address several challenges faced by traditional land-based data centers. One of the primary reasons is the growing concern over the environmental impact of data centers. Traditional data centers consume vast amounts of energy for cooling and operation, contributing to significant carbon emissions.
Moreover, the cost of land and the limitations on available space in urban areas make it increasingly difficult to build new data centers. Underwater data centers offer a solution by utilizing the vast and relatively untapped ocean space. This approach also provides an opportunity to bring data centers closer to coastal cities, reducing latency and improving service delivery for end-users.
Another compelling reason is disaster resilience. Underwater data centers can be designed to withstand natural disasters such as earthquakes and tsunamis, offering greater protection for critical data and infrastructure compared to their land-based counterparts.
Advantages of Underwater Data Centers
There are several advantages to deploying underwater data centers:
- Energy Efficiency: The natural cooling properties of seawater significantly reduce the energy required for cooling, leading to lower operational costs and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Space Utilization: Utilizing ocean space alleviates the pressure on land resources, allowing for the expansion of data centers without the need for large land acquisitions.
- Proximity to Coastal Cities: Placing data centers underwater near coastal areas can reduce latency, providing faster data access for users in those regions.
- Disaster Resilience: Underwater data centers can be designed to be more resilient to natural disasters, ensuring higher data protection and continuity of service.
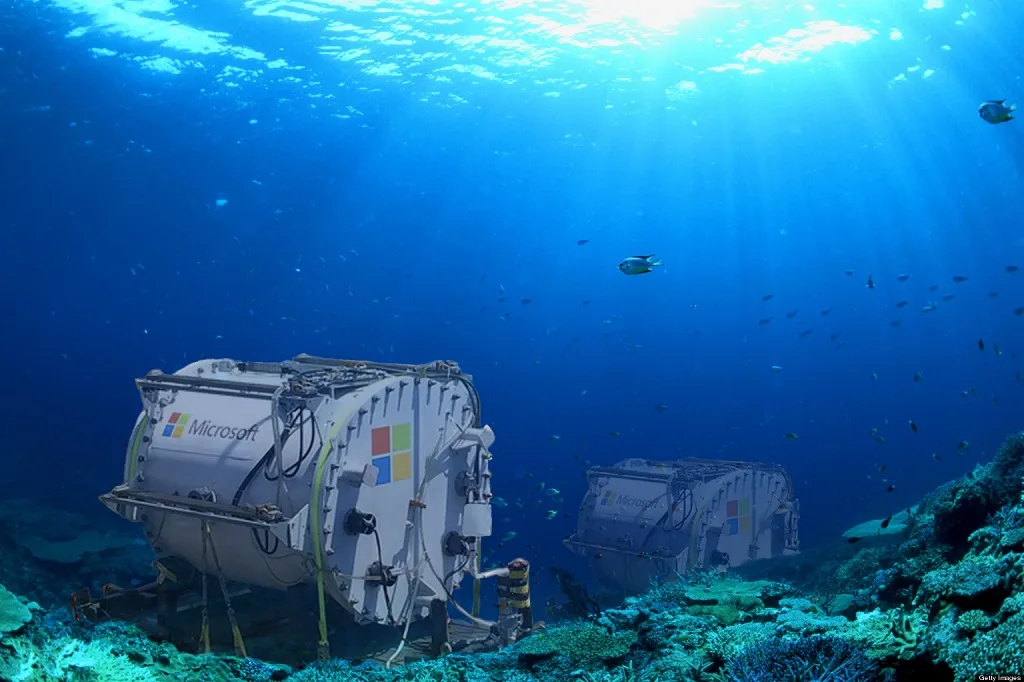
Disadvantages of Underwater Data Centers
Despite their benefits, underwater data centers also present some challenges:
- Deployment and Maintenance: Installing and maintaining underwater data centers is more complex and costly compared to traditional data centers. Specialized equipment and expertise are required for underwater operations.
- Environmental Impact: While underwater data centers aim to be more sustainable, there are concerns about their impact on marine ecosystems. Careful planning and environmental assessments are necessary to mitigate potential harm.
- Technical Challenges: Ensuring reliable connectivity and power supply in underwater environments poses significant technical challenges. Robust solutions are needed to address these issues.
The Future of Underwater Data Centers
The concept of underwater data centers is still in its early stages, but the potential for innovation and growth is substantial. As technology advances, we can expect to see more efficient and sustainable designs that overcome current challenges. Companies like Microsoft have already conducted successful pilot projects, demonstrating the feasibility of underwater data centers.
Future developments may include improvements in underwater robotics for maintenance, enhanced environmental monitoring systems, and more integration with renewable energy sources. As the demand for data continues to grow, underwater data centers could become a key component of the global data infrastructure, offering a sustainable and resilient solution for the future.
In conclusion, underwater data centers represent a promising direction for the future of data storage and processing. By leveraging the natural cooling properties of the ocean and addressing the limitations of land-based data centers, this innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize the industry. As technology continues to evolve, we can look forward to more sustainable and efficient data center solutions that meet the growing demands of the digital age.